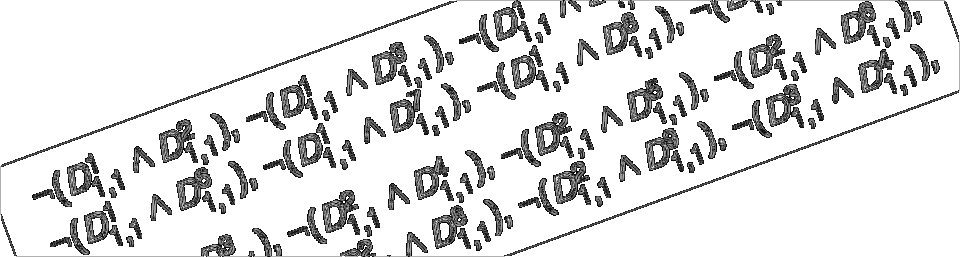@InProceedings{moserKirstenDoerre2024,
title = {{SoK}: Mechanisms Used in Practice for Verifiable
Internet Voting},
author = {Florian Moser and
Michael Kirsten and
Felix D{\"{o}}rre},
year = {2024},
month = oct,
booktitle = {9th International Joint Conference on Electronic
Voting ({E-Vote-ID} 2024)},
pages = {141--162},
venue = {Tarragona, Spain},
eventdate = {2024-10-02/2024-10-04},
series = {Lecture Notes in Informatics},
volume = {P-359},
number = {Track 3: Election and Practical Experiences},
publisher = {Gesellschaft f{\"{u}}r Informatik},
editor = {Melanie Volkamer and
David Due{\~n}as-Cid and
Peter R{{\o}}nne and
Jurlind Budurushi and
Michelle Blom and
Adria Rodr{\'i}guez-P{\'e}rez and
Iuliia Spycher-Krivonosova and
Beata Martin-Rozumilowicz and
Oliver Spycher},
abstract = {Increasing demands for internet voting instigated the
deployment of a multitude of systems used in practice. Within
this work, we are interested in which security mechanisms are
currently used by vendors to implement verifiable and secret
elections.
We perform a systematic market study and review academic
literature, where out of 82 candidate systems, we find 29
internet voting systems that are both in active use and claim
to employ some form of verifiability. Thereof, we characterize
and systematize the 18 systems that provide sufficient
information to extract their security mechanisms relevant for
state-of-the-art verifiability and secrecy. Overall, we find
that only eight systems are well-documented, of which only a
few employ state-of-the-art mechanisms in all categories that
we consider.},
doi = {10.18420/e-vote-id2024_10},
url = {https://hal.science/hal-04686386}
}
SoK: Mechanisms Used in Practice for Verifiable Internet Voting
| Author(s): | Florian Moser, Michael Kirsten, and Felix Dörre |
|---|---|
| In: | 9th International Joint Conference on Electronic Voting (E-Vote-ID 2024) |
| Publisher: | Gesellschaft für Informatik |
| Series: | Lecture Notes in Informatics |
| Number: | Track 3: Election and Practical Experiences |
| Volume: | P-359 |
| Year: | 2024 |
| Pages: | 141-162 |
| URL: | https://hal.science/hal-04686386 |
| DOI: | 10.18420/e-vote-id2024_10 |
Abstract
Increasing demands for internet voting instigated the deployment of a multitude of systems used in practice. Within this work, we are interested in which security mechanisms are currently used by vendors to implement verifiable and secret elections. We perform a systematic market study and review academic literature, where out of 82 candidate systems, we find 29 internet voting systems that are both in active use and claim to employ some form of verifiability. Thereof, we characterize and systematize the 18 systems that provide sufficient information to extract their security mechanisms relevant for state-of-the-art verifiability and secrecy. Overall, we find that only eight systems are well-documented, of which only a few employ state-of-the-art mechanisms in all categories that we consider.